word2vec
Implementation of the first paper on word2vec
GitHub
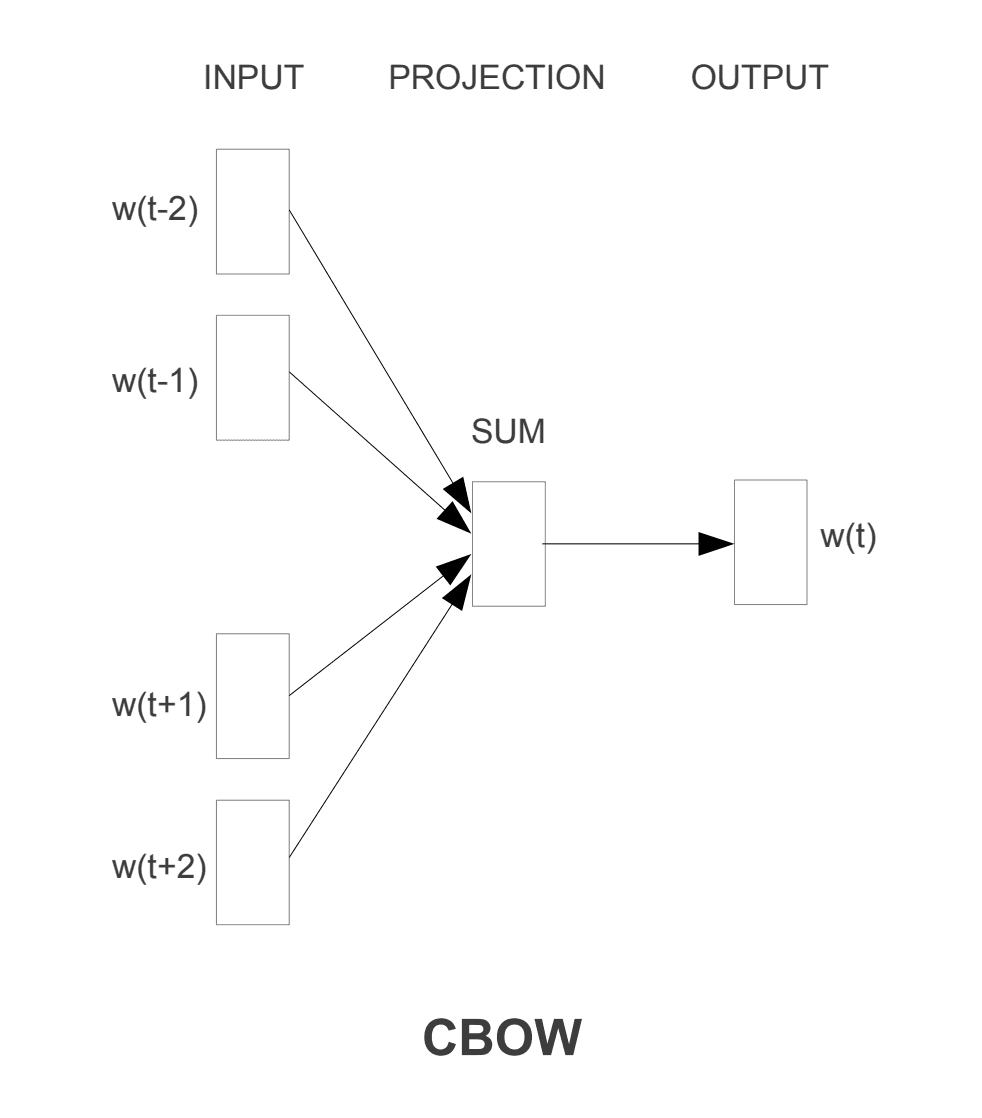
This is an implementation of the first paper on word2vec Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space. While there are 2 proposed model architecures in the paper (cbow & skipgram) I focused on the Continuous Bag-of-Words Model (CBOW), that predicts a words based on it's context.
Differences from the original paper:
Trained on WikiText2 and WikiText103 instead of Google News corpus. ( due to computational limitations ).
Context for both models is represented as 4 history and 4 future words.
After testing out various context lengths, 4 was by far the best performing given the limtied dataset used.
Plain Softmax was used instead of Hierarchical Softmax.
Large reduction in complexity.
Adam optimizer was used instead of Adagrad.
A much more up to date optimizer.
Trained for 5 epochs.
After testing out different variations, this gave me the best result.
Regularization applied: embedding vector norms are restricted to 1.
Helps to prevent overfitting, by adding a constraint to the model's loss function. Since the embedding vectors are constrained in their magnitude, the model might generalize better to unseen words or contexts. The regularization ensures that the embeddings do not react too strongly to any specific features of the training data.
Timeline
Jan. 2024
Team
Solo
Tech
Python
****
Disciplines
Natural Language Processing

word2vec
Implementation of the first paper on word2vec
GitHub
This is an implementation of the first paper on word2vec Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space. While there are 2 proposed model architecures in the paper (cbow & skipgram) I focused on the Continuous Bag-of-Words Model (CBOW), that predicts a words based on it's context.
Differences from the original paper:
Trained on WikiText2 and WikiText103 instead of Google News corpus. ( due to computational limitations ).
Context for both models is represented as 4 history and 4 future words.
After testing out various context lengths, 4 was by far the best performing given the limtied dataset used.
Plain Softmax was used instead of Hierarchical Softmax.
Large reduction in complexity.
Adam optimizer was used instead of Adagrad.
A much more up to date optimizer.
Trained for 5 epochs.
After testing out different variations, this gave me the best result.
Regularization applied: embedding vector norms are restricted to 1.
Helps to prevent overfitting, by adding a constraint to the model's loss function. Since the embedding vectors are constrained in their magnitude, the model might generalize better to unseen words or contexts. The regularization ensures that the embeddings do not react too strongly to any specific features of the training data.
Timeline
Jan. 2024
Team
Solo
Tech
Python
****
Disciplines
Natural Language Processing

word2vec
Implementation of the first paper on word2vec
GitHub
This is an implementation of the first paper on word2vec Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space. While there are 2 proposed model architecures in the paper (cbow & skipgram) I focused on the Continuous Bag-of-Words Model (CBOW), that predicts a words based on it's context.
Differences from the original paper:
Trained on WikiText2 and WikiText103 instead of Google News corpus. ( due to computational limitations ).
Context for both models is represented as 4 history and 4 future words.
After testing out various context lengths, 4 was by far the best performing given the limtied dataset used.
Plain Softmax was used instead of Hierarchical Softmax.
Large reduction in complexity.
Adam optimizer was used instead of Adagrad.
A much more up to date optimizer.
Trained for 5 epochs.
After testing out different variations, this gave me the best result.
Regularization applied: embedding vector norms are restricted to 1.
Helps to prevent overfitting, by adding a constraint to the model's loss function. Since the embedding vectors are constrained in their magnitude, the model might generalize better to unseen words or contexts. The regularization ensures that the embeddings do not react too strongly to any specific features of the training data.
Timeline
Jan. 2024
Team
Solo
Tech
Python
****
Disciplines
Natural Language Processing